The dynamic business environment of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) has become a nurturing hub for entrepreneurship and innovation. This environment is supported by the UAE government’s active backing of startups through initiatives such as Dubai Future Accelerators, Abu Dhabi Global Market’s Regulatory Laboratory (RegLab), and DIFC FinTech Hive. These initiatives facilitate collaboration between startups, government entities, and industry leaders. The UAE also offers a multitude of startup incubators, accelerators, and co-working spaces that foster an optimal setting for budding ventures.
Startup Genome reports that as part of its Entrepreneurial Nation initiative, the UAE Government aspires to nurture over 8,000 SMEs and startups by 2030. Furthermore, the government aims to cultivate a thriving startup ecosystem, with the ambitious target of fostering the emergence of 20 startups valued at over $1 billion each by 2031. Notably, the tech and fintech sectors have experienced a surge in startups, driven by the government’s commitment to diversifying the economy beyond oil reliance. However, despite these advantages, establishing and expanding a startup in this landscape presents its own set of challenges.
Business Setup Procedures
A major hurdle for UAE startups is dealing with intricate business setup procedures. The legal system, particularly for foreign entrepreneurs, is multifaceted, involving federal and emirate-level laws, regulations, and licenses. To navigate this complexity, you need to choose the correct legal setup, get the necessary permits, and adhere to sector-specific rules.
Intellectual Property Protection
Startups often rely heavily on their innovations, brand identity, and intellectual property to differentiate themselves in the market. Securing and protecting intellectual property rights, such as trademarks, patents, and copyrights, is crucial to prevent unauthorized use and infringement. The process of registering IP rights in the UAE can be time-consuming. Delays in obtaining registration certificates or trademarks can leave a startup vulnerable to IP infringement.
Employment Law Compliance
Growing startups encounter challenges in recruiting and managing their workforce. The UAE’s Federal Decree-Law No. 33 of 2021 is the governing statute, safeguarding employee rights and employer responsibilities. It applies universally, from small startups to large multinational corporations. All businesses with UAE employees must adhere to these labor regulations, necessitating continual policy adjustments to stay aligned with evolving legal requirements.
Contractual Agreements and Commercial Transactions
Startups often enter into contracts with suppliers, partners, and clients. Creating clear and comprehensive contractual agreements is essential to prevent potential misunderstandings and disputes. In the UAE, contractual agreements and commercial transactions are important to startups’ operations, serving as crucial tools to establish business relationships, outline rights and obligations, and protect the interests of all involved parties. Precise drafting of contracts is necessary to avoid confusion and conflicts by clearly defining terms and conditions.
Funding and Investment
Access to funding is a critical aspect of startup growth. Startups often struggle to access sufficient capital, especially during their early stages. Traditional funding sources like banks may be hesitant to lend to new and unproven businesses, leading to limited financing options. In recent years, alternative methods of funding have gained popularity among startups, surpassing traditional bank loans as the go-to option. For instance, for smaller funding needs, the UAE offers a variety of microloan companies, along with the rising trend of crowdfunding sites that have become increasingly favored options. According to a recently published report, over 30 percent of funding rounds within the Middle East and North Africa region are linked to startups headquartered in Dubai. The findings come from a new study conducted by the Dubai Chamber of Digital Economy, focusing on the city’s venture capital environment. The report highlights that an impressive 87 percent of all funding rounds for companies based in the UAE are directed toward startups located within Dubai.
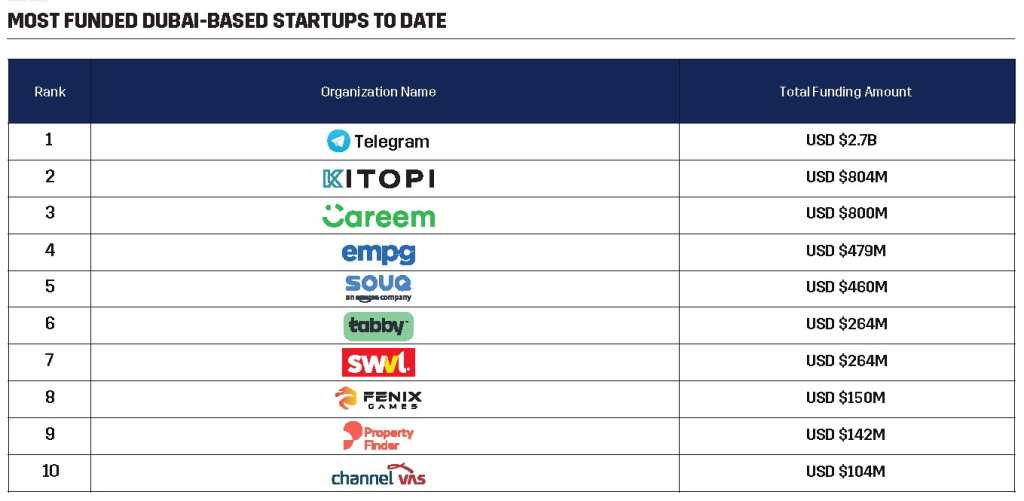
Image Source: Dubai Digital Economy, Dubai’s Digital Economy and Its Expanding Startup Ecosystem, 2023.
Regulatory Compliance and Licensing
The UAE enforces industry-specific rules that startups must comply with to avoid legal issues and penalties. Aligning with global standards, the UAE has enacted measures to enhance its economic framework. This includes laws addressing Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing of Terrorism and Illegal Organizations (AML-CFT), Value Added Tax (VAT), Economic Substance Regulations (ESR), Ultimate Beneficial Ownership (UBO), and the newly implemented UAE Corporate Tax.
Conclusion
In the intricate field of UAE’s growing startup ecosystem, legal challenges form a formidable thread. Startups navigating through regulations, intellectual property protection, contractual agreements, and compliance requirements face a difficult path. Engaging with a knowledgeable and experienced law firm can prove invaluable for startups, as legal support helps them overcome obstacles, and establish a solid foundation for sustainable growth. By partnering with law firms that understand the unique needs of startups, entrepreneurial ventures in the UAE can focus on innovation and expansion with confidence, knowing their legal interests are well-protected. Offering tailored counsel, proactive compliance strategies, and adept resolutions to legal complexities, Strohal Legal Group assumes a pivotal role as your essential partner for your startup enterprise. Our extensive familiarity with the intricate UAE business landscape positions us to support and steer your journey through the UAE’s entrepreneurial landscape.
Download the article here.